ProTip
Don't worry about the Nouveau conflict thing that you might heard of, NVIDIA's installer will take care of it. If you get stuck with some version conflicts, don't spend too much time to fix it. You could just reinstall Ubuntu and start from scratch within minutes, provided you have some understanding of what went wrong. Also note that we will be using latest version of everything, so we'd have to do a few intense builds.The Essentials
Let's start by updating repos and installing essentials for NVIDIA drivers.sudo apt-get update -y sudo apt-get upgrade -y sudo apt-get install -y build-essential linux-source sudo apt-get install -y linux-source linux-headers-`uname -r` sudo apt-get install -y linux-image-extra-virtual
Installing NVIDIA Binary Drivers
Then download the appropriate version of driver for your graphic card from NVIDIA or GeForce to your local machine.cd ~/ wget -O ~/nvidia.run http://us.download.nvidia.com/XFree86/Linux-x86_64/361.42/NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-361.42.runFor a cleaner install, let's remove any existing NVIDIA drivers
sudo apt-get remove --purge nvidia* sudo apt-get autoremoveReboot and enter Ubuntu recovery mode, activate failsafeX and then enter the terminal. Go to the download directory and change permissions to execute and run the installer.
sudo service lightdm stop cd ~/ chmod +x nvidia.run sudo sh nvidia.runIf it says something like "The distribution-provided pre-install script failed! Are you sure you want to continue?" Answer yes and proceed with the install.
Installing CUDA 7.5
Visit CUDA download page and get the "runfile (local)" version of the installer as other versions might not allow you to exclude driver installation. It's a 1GB+ file.wget -O ~/cuda.run http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/7.5/Prod/local_installers/cuda_7.5.18_linux.run sudo sh cuda.runThe installer will prompt for a few things, accept all except for "CUDA Driver installation" - don't accept it. We have already installed the latest version of driver in our previous step. If we accept it, it might overwrite our previous install with a different version and cause version conflicts, so don't.
Installing Miniconda
We'll be using Miniconda to manage Python 3 packages, as I had bad experience trying to get it work with default Ubuntu pip/apt-get packages.wget -O ~/miniconda.sh https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh bash ~/miniconda.sh -b -p $HOME/miniconda export PATH="$HOME/miniconda/bin:$PATH"Let's create a virtual environment specifically for tensorflow in Miniconda
conda and install necessary packages.
conda create -n tensorflow python=3.5 source activate tensorflow conda install python=3.5 pip numpy -yIf you're getting errors that there's no
conda available, exit the terminal and try again.
Installing cuDNN 7.5
Now NVIDIA doesn't allow us to directly download cuDNN (wget) to our machine from their site, you'll get Access Denied if you tried to do so. So we will have to download cuDNN from the browser and move it our working directory. On the download page NVIDIA will ask you to fill up a survery, it's not compulsory - just click the "Proceed To Downloads" button if you are not in a good state of mind to answer a survey rationally, at this point. Just extract the file and move the contents to /usr/local.
mv ~/Downloads/cudnn-7.5-linux-x64-v5.0-rc.tgz /tmp cd /tmp tar -xzf cudnn-7.5-linux-x64-v5.0-rc.tgz sudo cp /tmp/cuda/lib64/* /usr/local/cuda/lib64 sudo cp /tmp/cuda/include/* /usr/local/cuda/include
Installing Java 8
Latest version of Bazel requires Java 8 but as of nowsudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk doesn't seem to lead nowhere. So we will have to get it from some private package.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:openjdk-r/ppa sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y openjdk-8-jdkNow we have to change default Java version to the latest one we've just installed.
sudo update-alternatives --config java sudo update-alternatives --config javacSelect the latest Java version from the list, usually it's the option #2.
Selection Path Priority Status ------------------------------------------------------------ 0 /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java 1071 auto mode 1 /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java 1071 manual mode * 2 /usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java 1069 manual
Installing Bazel
Bazel is Google's own build tool that will help us compile TensorFlow. Should be straight forward, but be cautious of the permission issues.cd /tmp git clone https://github.com/bazelbuild/bazel.git cd bazel ./compile.sh sudo cp /tmp/bazel/output/bazel /usr/bin export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64" export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cudaFor some reasons, if you're getting the following error
JDK version (1.7) is lower than 1.8, please set $JAVA_HOME.you can try to explicitly specify the Java path by
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/
Installing TensorFlow
Finally let's compile and install TensorFlow. This might take a while to finish.cd /tmp git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow cd tensorflow TF_UNOFFICIAL_SETTING=1 ./configureExcept for the one below, leave everything to their defaults. As message mentions, visit the NVIDIA page check your graphic card's "Compute Capability" value. For instance, according to the page, my GTX 970's value is 5.2, so specify it accordingly. Better not to accept the default.
Please specify a list of comma-separated Cuda compute capabilities you want to build with. You can find the compute capability of your device at: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus. Please note that each additional compute capability significantly increases your build time and binary size. [Default is: "3.5,5.2"]: 5.2Now let the waiting game begin (and hopefully you won't run into disk space issues).
bazel build -c opt --config=cuda //tensorflow/cc:tutorials_example_trainer bazel build -c opt --config=cuda //tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package bazel-bin/tensorflow/tools/pip_package/build_pip_package /tmp/tensorflow_pkgNow that we have successfully build the .whl file, let install it via pip. Change directory to the output folder and look for the file name, in my case it was tensorflow-0.8.0rc0-py3-none-any.whl.
cd /tmp/tensorflow_pkg/ ls pip install --upgrade /tmp/tensorflow_pkg/tensorflow-0.8.0rc0-py3-none-any.whlNow let's check if everything is working fine.
cd /tmp/tensorflow/tensorflow/models/image/cifar10/ python cifar10_multi_gpu_train.py
Note
Everytime you want to use tensorflow you have activate the environment bysource activate tensorflow #(tensorflow)$ # Your prompt should change.When you are done using TensorFlow, deactivate the environment.
source deactivateI hope you find this useful and helped you save a couple of hours. Please leave me a message if there's any issues.
Troubleshooting
When you're testing TensorFlow, if it says that there's no GPU, try installing linux headers again byapt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)Also do the same if you're getting any of the errors below:
cat /proc/driver/nvidia/version cat: /proc/driver/nvidia/version: No such file or directory sudo nvidia-modprobe modprobe: ERROR: ../libkmod/libkmod-module.c:809 kmod_module_insert_module() could not find module by name='nvidia_352' modprobe: ERROR: could not insert 'nvidia_352': Function not implementedIf you're still having issues with NVIDIA drive, please refer to NVIDIA's Documentation
Every time after you restart the machine, you'll have to update the env variables.
export PATH="$HOME/miniconda/bin:$PATH" export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64" export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/Or you can permanently add it to
~/.bashrc
echo "export PATH=$HOME/miniconda/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64/" >> ~/.bashrcIf you want to check version of the NVIDIA driver installed, you can try any of the following:
lspci -nnk | grep -iA2 vga lspci | grep -i nvidia dpkg -l | grep nvidia dpkg -l | grep ii | grep -i nvidia nvidia-settings -q NvidiaDriverVersion
References
- http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-getting-started-guide-for-linux/
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/NvidiaManual
- https://help.ubuntu.com/community/BinaryDriverHowto/Nvidia
- http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2081649
- http://conda.pydata.org/docs/help/silent.html
- http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/cudnn/secure/v5/rc/cudnn_install.txt?autho=1461438353_9d110e75f21326804dcc3b7194b8c689&file=cudnn_install.txt
- https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/1158
- https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started
- https://devtalk.nvidia.com/default/topic/920308/how-to-install-cuda-7-5-with-the-newest-nvidia-driver-361-28-/
- https://devtalk.nvidia.com/default/topic/884586/linux/failed-to-install-cuda-7-5-in-ubuntu-14-04-lts/
 Last week Google
Last week Google  So I ran Crystal Disk benchmark on my Samsung 850 EVO SSD and it was crawling like a boneless snail. After some googling, I realized my Windows 10 was still running on IDE mode and all we have to do is change it to AHCI, which is basically a faster mode of operation than the legacy IDE. To do that:
So I ran Crystal Disk benchmark on my Samsung 850 EVO SSD and it was crawling like a boneless snail. After some googling, I realized my Windows 10 was still running on IDE mode and all we have to do is change it to AHCI, which is basically a faster mode of operation than the legacy IDE. To do that: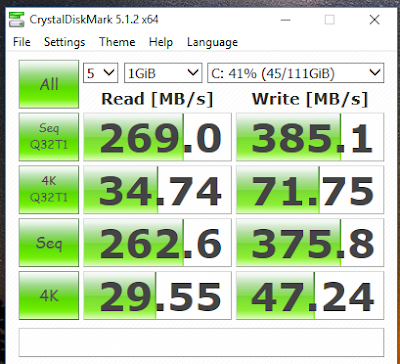
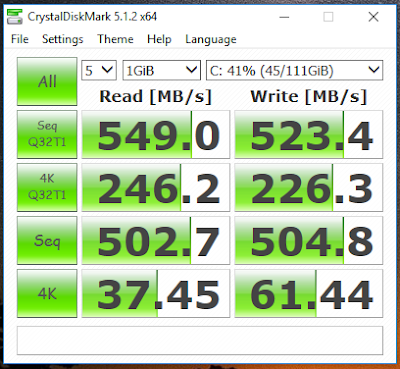
 I was able to install Neverware CloudReady on my hard drive without errors, but when I plug out the installer USB and try to boot the OS, I was getting a "No bootable device -- insert boot disk and press any key" error. After tons of googling, apparently my legacy Intel Desktop Board does not support GPT well, so we'll have to manually set the Protective Master Boot Record (PMBR) flag using parted the utility.
I was able to install Neverware CloudReady on my hard drive without errors, but when I plug out the installer USB and try to boot the OS, I was getting a "No bootable device -- insert boot disk and press any key" error. After tons of googling, apparently my legacy Intel Desktop Board does not support GPT well, so we'll have to manually set the Protective Master Boot Record (PMBR) flag using parted the utility.